-
Innovative EEG brainwave monitors for
- Sports performance, psychology & coaching
- Neuro feedback, hypnotherapy & cognitive therapies
- Neuroscience research
- EEG-based games for neuro feedback therapy, training and entertainment
PDF download of our brochure on therapy use PDF download of our brochure on sports use Some useful links outside our website
EEG - General principles
Brainwaves are naturally occurring electrical signals in the brain which are caused by the neurons 'firing'. These pulses can be measured on the surface of the head using an EEG. There are five distinct frequency ranges of brainwaves that indicate different brain (or mind) states. In ascending frequency order these are known as delta, theta, alpha, beta and gamma and they are correlated to different levels of awareness, focus and excitation in the brain.
EEG brainwave patterns can be an indication of concentration or 'focus'. Sometimes this is known as being 'in the zone'. Many people, especially sports men and women, routinely try to optimise their brainwaves to improve their performance. Focus may be related to an increase in the alpha brain wave frequency (which occurs at approximately 8 to 12 Hz). Performers and musicians can show a higher level of both alpha and theta brainwaves when they are performing at their best.
EEG is also used to monitor hypnosis, states of consciousness, for meditation and relaxation. See publications and links.
How EEGs work
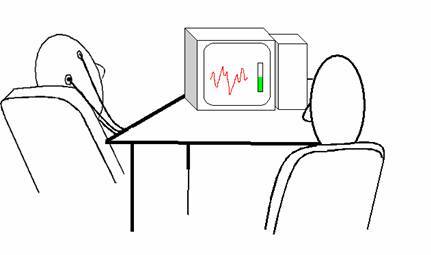
An EEG device records electrical signals from the brain, specifically postsynaptic potentials of neurons originating from the cerebral cortex, through electrodes that are attached to the subject's scalp.
The electrodes attached to the subject's scalp transmit the electrical signals produced by the brain to the EEG monitor. Since these electrical signals are very small (of the order of 10s of microvolts) the EEG acts as an amplifier, typically amplifying them by 10,000 times, as well as a device to measure them.
An EEG lets a practitoner view, in real time, and record electrical impulses from the brain and observe changes to those impulses. This can indicate the general mind state of the subject being monitored.
EEGs are usually large, heavy, expensive pieces of equipment, that require extensive operator training & are used in special rooms in hospitals etc. They generally require the subject to be laying down or sitting and to remain still during the test. None of this is the case with the Alpha-Active EEG.
- Read our brochure on use in therapies - PDF download - New window -Please allow a few moments
- Read our brochure on use in sports - PDF download - New window - Please allow a few moments

